A Practical Guide to the Saga Pattern in Spring Boot Microservices
Modern microservices are small, autonomous, and independently deployable — but this also creates a huge problem.
Typical pharmacy prescription management - payments, banking, logistics, supply-chain, or booking systems perform operations across multiple microservices
- Create Order
- Reserve Inventory
- Process Payment
- Create Shipment
- Update Loyalty Points
Each runs in its own database, service, and network boundary.
If one operation fails halfway, the entire business flow should not leave the system in an inconsistent state.
This is where the Saga Pattern becomes essential.
What is a Saga? Why Not Use ACID?
A Saga is a sequence of local transactions. \n Each local transaction updates data within one service and publishes an event to trigger the next step.
If a failure occurs:
- The Saga triggers compensation actions to undo previously completed steps.
Why does ACID (2PC) not work in microservices?
| Problem | Explanation | |:---:|:---:| | 2PC is blocking | If the coordinator crashes, everything hangs. | | Microservices have independent DBs | No shared commit log across distributed DBs. | | Scales poorly | Locks span distributed systems. | | Cloud services do not support XA transactions | DynamoDB, S3, Mongo, Kafka, RDS, etc. |
A Saga avoids these issues with event-driven or orchestrated compensation logic.
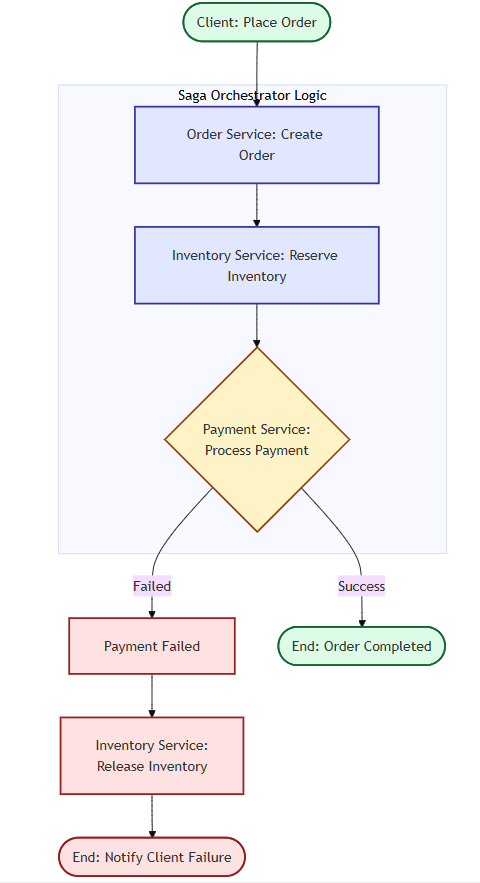
Saga Architecture Diagram:
\ 
1. Use Case: Pharmacy Prescription Order Processing
Scenario
Imagine a Pharmacy Prescription Online platform where a customer places an order for a product.
The system involves three independent services:
- Order Service – Creates the order record.
- Inventory Service – Reserves the product in stock.
- Payment Service – Charges the customer.
Problem Without Saga
If one of these steps fails (e.g., payment fails), the previous steps might leave the system in an inconsistent state:
- Order created
- Inventory reserved
- Payment failed
- Result: Inventory stuck, order incomplete, manual intervention required.
This is unacceptable in enterprise systems, especially when multiple microservices interact.
Solution With Saga
Using a Saga Orchestration Pattern, each service executes its local transaction, and in case of failure, compensation actions roll back previous steps
- Step 1: Order Service creates an order.
- Step 2: Inventory Service reserves stock.
- Step 3: The payment service charges the customer.
- Failure Handling: If payment fails, the orchestrator calls the Inventory Service to release stock.
This ensures business-level consistency across services.
2. Why We Need the Saga Pattern
- Distributed Microservices: Traditional ACID transactions cannot span multiple microservices.
- Eventual Consistency: Ensures consistent outcomes without requiring global resource locking.
- Fault Tolerance: Automatically rolls back previous steps if a later step fails.
- Cloud-Native: Works seamlessly with scalable services in cloud environments.
Loose Coupling: Each service remains independent, communicating only through APIs.
3. Advantages of Using Saga
- Reliability: Compensating transactions prevent data inconsistencies.
- Scalability: Each service can scale independently; orchestration is centralized.
- Resilience: Handles partial failures gracefully.
- Business-Level Consistency: Focuses on correct business outcomes, not strict database consistency.
- Monitoring and Debugging: The central orchestrator provides clear logs of each transaction step.
4. Step-by-Step Explanation of the Script
Below is a detailed walkthrough of the key script components from your Spring Boot Saga project.
4.1 Order Model (Order.java)
\
package com.example.orderservice; public class Order { private Long id; private String product; private String status; public Order() { // default constructor (required for Jackson) } public Order(Long id, String product, String status) { this.id = id; this.product = product; this.status = status; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getProduct() { return product; } public void setProduct(String product) { this.product = product; } public String getStatus() { return status; } public void setStatus(String status) { this.status = status; } }
-
Purpose: Represents an order.
-
Business Logic: Stores the product name, order ID, and status (CREATED, CANCELLED, COMPLETED).
4.2 Order Controller (OrderController.java)
\
package com.example.orderservice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("/orders") public class OrderController { @PostMapping public Order create(@RequestParam("product") String product) { return new Order(1L, product, "CREATED"); } @PostMapping("/cancel") public String cancel() { return "ORDER_CANCELLED"; } @PostMapping("/complete") public String complete() { return "ORDER_COMPLETED"; } }
\
-
Endpoints
-
POST /orders → Creates an order.
-
POST /orders/cancel → Cancels an order (used for compensation).
-
POST /orders/complete → Marks order completed.
-
Why it works with Saga: Endpoints are simple, predictable, and return either the object or a status string for orchestration.
4.3 Inventory Controller (InventoryController.java)
\
package com.example.inventoryservice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("/inventory") public class InventoryController { @PostMapping("/reserve") public boolean reserve(@RequestParam("product") String product) { return !"FAIL".equals(product); } @PostMapping("/release") public void release(@RequestParam("product") String product) {} }
\
-
Purpose: Reserves product in stock, releases it if payment fails.
-
Logic: Simulates success/failure. In enterprise systems, this would check actual stock in a database.
\ 4.4. Payment Controller (PaymentController.java)
\
package com.example.paymentservice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("/payments") public class PaymentController { @PostMapping("/pay") public boolean pay(@RequestParam("amount") double amount) { return amount <= 5000; } @PostMapping("/refund") public void refund(@RequestParam double amount) {} }
\
-
Purpose: Processes payment and simulates failure for testing.
-
Why it works in Saga: Returns a Boolean indicating success/failure, allowing the orchestrator to trigger compensations.
4.5. Saga Orchestrator (SagaController.java)
\
package com.example.sagaorchestrator; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @RestController @RequestMapping("/saga") public class SagaController { private final RestTemplate rest = new RestTemplate(); @PostMapping("/order") public String place(@RequestParam("product") String product, @RequestParam("amount") double amount) { Object order = rest.postForObject( "http://localhost:8081/orders?product=" + product, null, Object.class ); if (order == null) { return "Order creation failed"; } Boolean inventory = rest.postForObject( "http://localhost:8082/inventory/reserve?product=" + product, null, Boolean.class ); if (inventory == null || !inventory) { return "Inventory failed"; } Boolean payment = rest.postForObject( "http://localhost:8083/payments/pay?amount=" + amount, null, Boolean.class ); if (payment == null || !payment) { rest.postForObject( "http://localhost:8082/inventory/release?product=" + product, null, Void.class ); return "Payment failed, compensated"; } return "Order completed successfully"; } }
\
- Flow Explained
- Order creation → First step, must succeed to proceed.
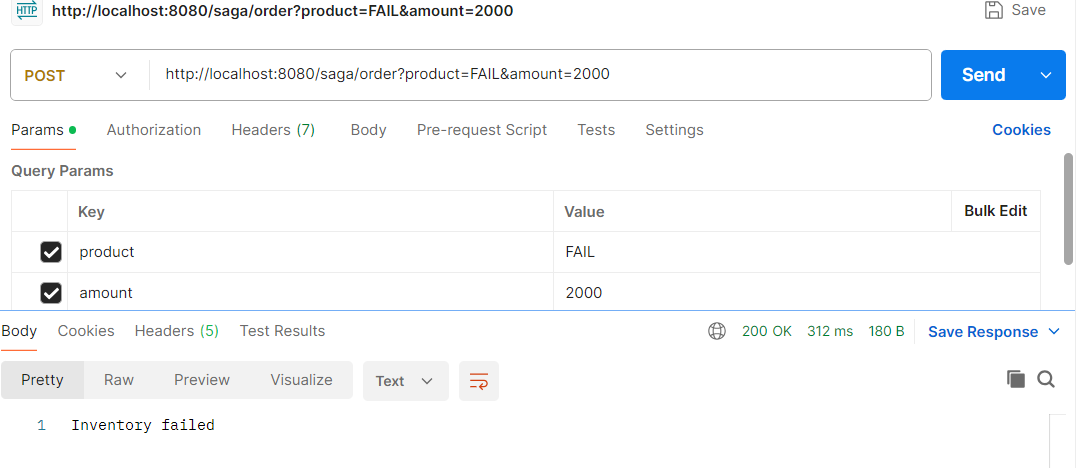
- Inventory reservation → If it fails, the saga stops.
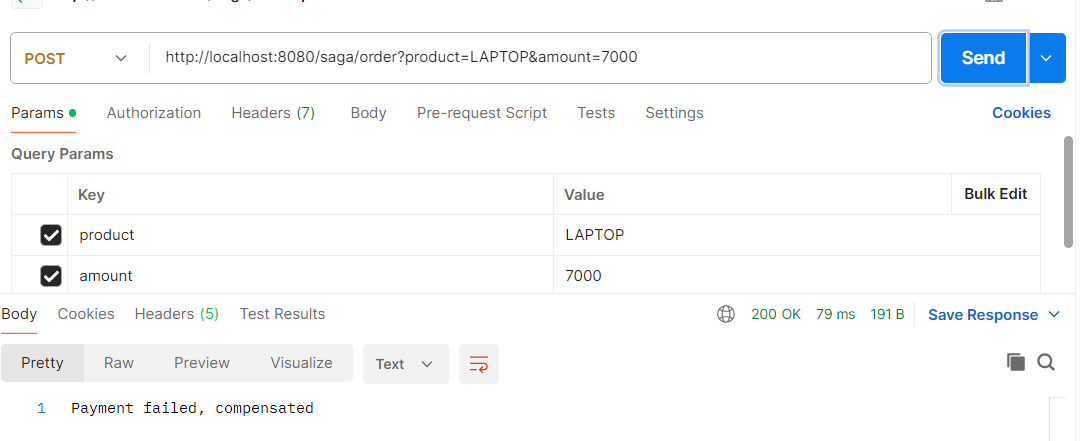
- Payment processing → If it fails, the orchestrator triggers inventory release (compensation).
- Success → Returns a success message.
Enterprise Ready: Demonstrates clear orchestration, compensation, and business-level consistency.
\ 4.6 Verification of Outputs
\
-
Success Case
\
- Payment Failure Case
\ 
\
- Inventory Failure Case:
\ ** 
5. Advantages Highlighted
- Fault-Tolerant: Automatically compensates failed transactions.
- Business Consistency: Ensures the order state and inventory are always consistent.
- Scalable: Each service runs independently.
- Cloud-Native Ready: Can run on Kubernetes or any cloud environment.
- Enterprise Applicable: Matches real-world systems in healthcare, banking, and data platforms.
6. Why Enterprises Need This Pattern
- In distributed systems, manual rollback is error-prone.
- Saga ensures automatic recovery, reducing downtime.
- Prevents inconsistent data in multi-service workflows.
- Supports asynchronous processing, improving performance and scalability.
\
You May Also Like

Will XRP Price Increase In September 2025?

Ripple IPO Back in Spotlight as Valuation Hits $50B
