How much profit can the “1:1 printing right” of stablecoins bring?
Written by: RWA Knowledge Circle
1. Stablecoins: The “Private Money Printing Machine” of the Digital Age
Over the past year, "stablecoin" has been one of the hottest buzzwords in the capital markets. A stablecoin is a digital currency pegged to a fiat currency, theoretically trading at a 1:1 ratio with the fiat currency and backed by real assets.
This raises the question: If large cross-border e-commerce companies issue stablecoins to reduce transaction costs and potentially save tens of millions of yuan annually, that's reasonable. However, in reality, stablecoins are often issued by blockchain platforms and digital service providers. So, how much profit can this "1:1 money printing power" actually generate?
Don't underestimate this business. The global stablecoin market landscape is clear: USDT holds a 60% market share, while USDC holds 25%. Tether, the issuer of USDT, has even made headlines: its average employee salary ranks second globally. Bloomberg also reports that it is considering selling a 3% stake for $15-20 billion, valuing it at $500 billion, comparable to OpenAI and SpaceX.
Tether, why is it worth this price?
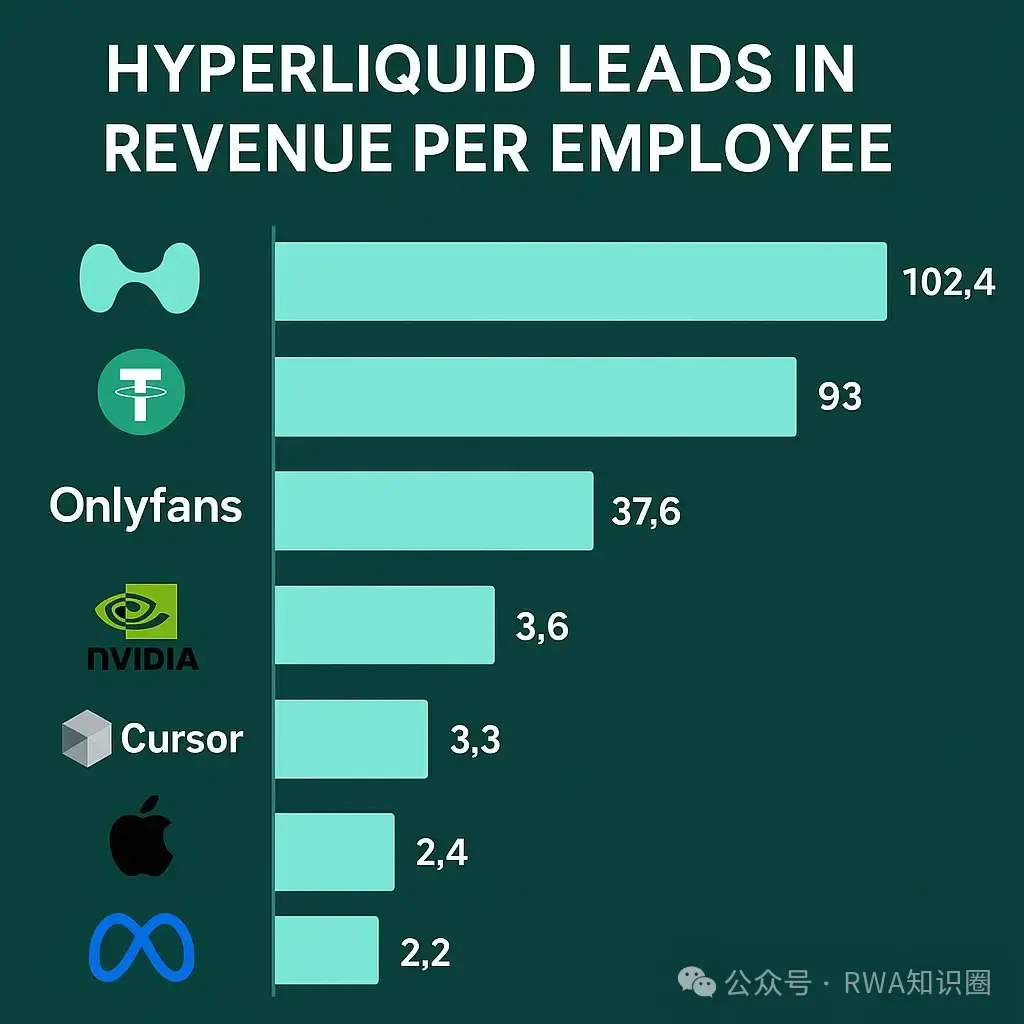
(Ranking of average salary of global companies)
2. The “Money Printing Logic” of Stablecoins
Traditional banks profit by accepting deposits and lending them out to earn a profit margin. Stablecoin issuers, on the other hand, collect US dollars and mint them into tokens on the blockchain. The money in hand is the source of profit.
Circle (USDC issuer): It has a stable operating style and mainly invests in low-risk assets such as US Treasury bonds and cash after receiving funds to ensure a 1:1 exchange rate with the US dollar.
Tether (USDT issuer): This model is more aggressive, currently holding $100 billion in reserves and earning over $4 billion annually from interest alone. Net profit is projected to reach $13.7 billion in 2024, with a profit margin of 99%.
Tether's portfolio includes not only cash and US Treasury bonds, but also Bitcoin and equity investments, spanning payment infrastructure, renewable energy, artificial intelligence, tokenization, and other fields. To some extent, Tether no longer resembles a simple stablecoin company, but more like a top investment bank and asset management giant.
3. The “Stablecoin War” of DeFi Protocols
Once the “printing money model” was discovered to be so profitable, it naturally attracted countless imitators. Many DeFi protocols have joined the stablecoin war:
MakerDAO’s DAI: One of the First Successful Decentralized Stablecoins
Innovation: It was the first to include U.S. Treasury bonds in its reserves, and at one point held more than $1 billion in short-term Treasury bonds.
Revenue Distribution: Excess revenue goes into a surplus buffer, which is then used to repurchase and burn MKR governance tokens. MKR is no longer just a "governance voting right," but is directly tied to cash flow, becoming an "equity token" with real value.
Frax: A small but focused "fine money printing machine"
Frax's overall scale is not large, and its circulation volume has been maintained below US$500 million for a long time, but its design is extremely sophisticated.
Income distribution:
- A portion is used to destroy FRAX tokens to maintain scarcity;
- A portion is allocated to stakers to enhance user stickiness;
The remaining portion is invested in the sFRAX vault, which tracks the Federal Reserve interest rate, which is equivalent to providing users with a product that "follows U.S. Treasury returns."
Although its scale is far smaller than Tether, Frax can still generate tens of millions of dollars in revenue each year, making it a representative example of "small scale and high efficiency".
Aave’s GHO: An extension of DeFi lending
The well-known lending protocol Aave launched its own stablecoin GHO in 2023.
Model: When users borrow GHO, the interest paid goes directly to Aave DAO instead of to external institutions.
Income distribution:
- approximately $20 million in interest income annually;
- Half of this amount is distributed to AAVE token stakers, and the other half remains in the DAO treasury for community governance and development.
- The current scale of GHO is approximately US$350 million, but its logic is to deeply integrate stablecoins with lending businesses to form a "vertical ecological closed loop."
It can be said that "Eight Immortals crossing the sea, each showing their magical powers", every stablecoin protocol is trying to build its own private money printing machine.
4. Hidden concerns: Is it really stable?
Although stablecoins reduce cross-border transaction costs and improve efficiency, they also pose many hidden risks:
- The anchored asset is not absolutely stable: Tether's reserves include Bitcoin, and once there is a sharp fluctuation, the stablecoin may "break away from the anchor".
- The revenue distribution process is not transparent: Many agreements claim that the revenue will be used for token repurchase or rewards, but the actual operation process is a "black box".
- Hedging strategies involve risks: The use of futures hedging models cannot theoretically guarantee 100% safety.
Compared with national credit endorsement, the "creditworthiness" of private stablecoins is always limited.
5. Why is Tether worth $500 billion?
Given the numerous risks, why is Tether still valued at $500 billion?
The answer is: stablecoins have become the infrastructure of the digital age.
It's not just a payment and settlement tool; it can also be embedded in scenarios like lending, trading, and RWA (real-world asset tokenization), providing a new channel for global capital circulation. Tether's high valuation actually reflects the market's huge expectations for the future of RWA.
Of course, the implementation of compliance supervision is still a key factor in determining how far stablecoins can go in the future.
Stablecoins, while seemingly just a cornerstone of the digital currency market, are actually a new form of "coinage" within the financial system. Whether it's Tether's $500 billion valuation or the proliferation of DeFi protocols, they remind us that the monetary landscape of the digital age is quietly being rewritten.
You May Also Like

Top Solana Treasury Firm Forward Industries Unveils $4 Billion Capital Raise To Buy More SOL ⋆ ZyCrypto

Fed Lowers Rates By 25bps: How Bitcoin And Crypto Prices Responded And What’s Next