Solana Sandwich Attack Returns: Priority Fees Become “Protection Fees”, and the “Dark Cycle” on the Chain Escalates Again
Author: Frank, PANews
When the Solana ecosystem fell into a trading volume decline due to the decline of MEME, a more hidden crisis is spreading. Recently, many community users complained that even if on-chain users paid priority fees (Tips), they still frequently encountered sandwich attacks, and some validator nodes were even accused of participating in them. This phenomenon exposed the deep contradiction of the Solana ecosystem - MEV (maximum extractable value) has evolved from a technical loophole to a systematic harvesting tool.
Data shows that the revenue of a sandwich attacker has soared from $30 million in two months to $287 million in six months, and users are forced to struggle between "being sandwiched" and "paying higher protection fees." Behind this crisis is the triple stranglehold of validator interest bundling, alienation of the priority fee mechanism, and collapse of user trust.
Industrialization of Sandwich Attacks: From Guerrilla Warfare to Assembly Line Harvesting
Previously, PANews conducted an in-depth investigation into the MEV situation on the Solana chain and exposed the most notorious sandwich attack robot on the chain at the time, which started with arsc and made a profit of more than 30 million US dollars in 2 months (Related reading: "Grabbing" 30 million US dollars in 2 months, Solana's largest sandwich attacker made 570,000 US dollars a day and aroused public anger )
Several months have passed. What is the current status of the sandwich attack on the Solana chain?
First of all, it is very regrettable that the sandwich attack on the Solana chain has not been restrained due to the community's condemnation and media exposure. Instead, it has changed to a new method and adopted a larger-scale attack matrix.
Taking the previously dug-up address Ai4zqY7gjyAPhtUsGnCfabM5oHcZLt3htjpSoUKvxkkt as an example, this address was finally used until November 15, 2024. According to PANews statistics, the address made a total profit of approximately US$287 million in the six months from May to November.
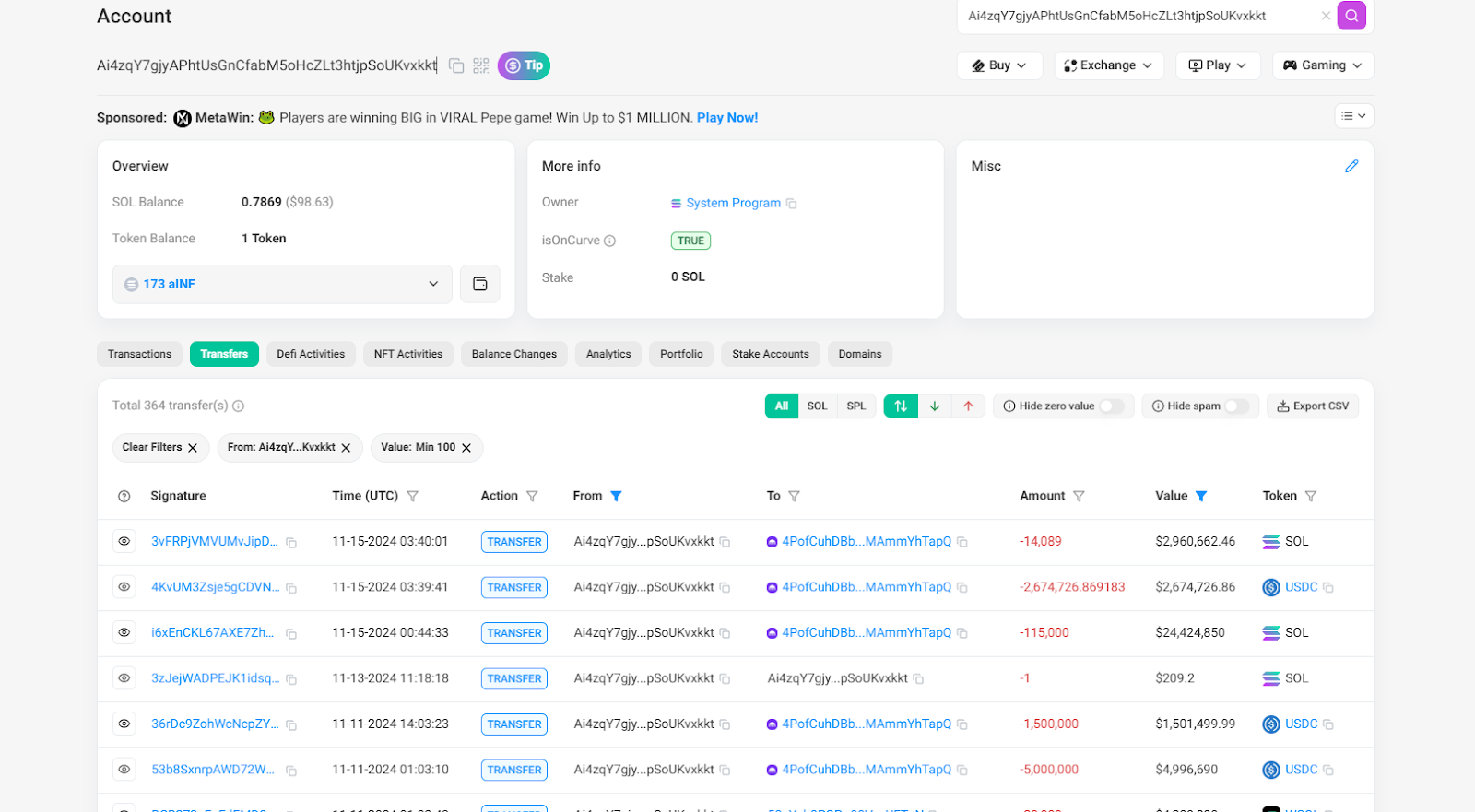
There have also been new changes in the attack methods. In order to avoid being tracked, the sandwich attack robot on the Solana chain has switched to a new address with a larger batch size. And a program has been established to execute the attack in batches.
Taking the program of this attack as an example, the number of addresses of this program is 77, and as of March 12, a total of 429,000 transactions have been carried out (because it is specifically used for sandwich attacks, all transactions can be regarded as attacks). Assuming that one attack requires two transactions, the program has carried out a total of 215,000 attacks.
Another address, 4vJfp62jEzcYFnQ11oBJDgj6ZFrdEwcBBpoadNTpEWys, carried out a total of 210,000 attacks in the past month, transferring a total of about 1.6 million US dollars to the exchange, with an average profit of 7.6 US dollars per transaction.
In fact, there are many more programs that carry out large-scale sandwich attacks every day than six months ago, but we cannot get the exact number because we cannot collect data.
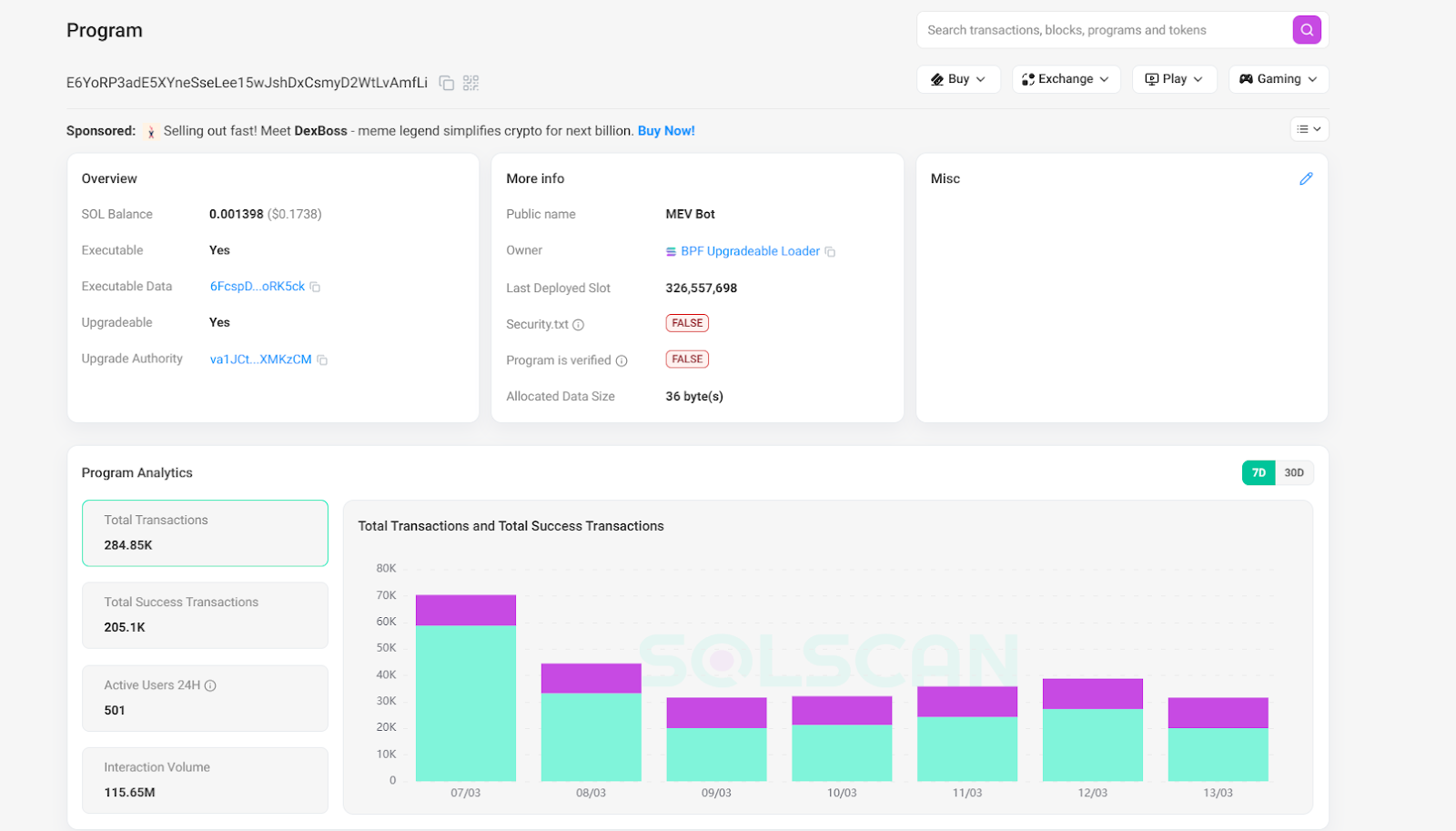
The embarrassment of priority fees: from "acceleration fees" to "protection fees"
Faced with increasingly frequent attacks, although users try to avoid risks through trading robots or increasing priority fees, the priority fee mechanism has been completely alienated - from a tool to improve transaction efficiency to a disguised "on-chain tax", further increasing the burden on users.
The ones who profit are the validator nodes that make profits from MEV income.
The SIMD-0228 proposal, which is currently under discussion, attempts to reduce the staking income of nodes, but the premise is that the proposer believes that the current MEV income is sufficient to maintain the expenses of these nodes.
Back to the topic of MEV, people will find a strange Möbius loop. The sandwich attack drives users to pay priority fees, which can increase node income, and some nodes participate in the sandwich attack. When several links are connected in series, the sandwich attacker's left and right harvesting strategy becomes the most profitable model on the Solana chain.
Users can only choose between "being squeezed and losing principal" and "paying a higher priority fee".
Of course, no one cares about this dark trick during the bull market, but during the bull market, users are more concerned about the wealth effect and major hacking incidents. For sandwich attacks or small RUG incidents, the parties involved can only blame themselves for their bad luck in most cases. The attackers just sit and wait to collect the money.
The collapse of trading volume has led to a shift in the clamp model: from "bundling" to "queue jumping"
But this logic is changing as the market declines. According to social media discussions and PANews' investigation, the cost of an effective sandwich attack is not low.
Among them, the biggest cost comes from the fact that the attacker has to deploy multiple validator nodes around the world to insert transactions in the first place. It should be noted that the logic here does not mean that the attacker's node must lead the block to implement the attack. The key is that when the attacker monitors the latest attackable transaction, the node closest to the node of the leader block must send the transaction to implement the operation. Generally speaking, it costs millions of dollars to deploy a complete set of attack node clusters.
Such costs, while ensuring that the attack brings a steady stream of income, also bring certain profit and loss pressure to the sandwich attacker. When the transaction volume on the chain gradually decreases, the attacker's income will also decline. And there will be stronger competition among attackers. Whoever can provide higher priority fees is likely to occupy a larger market share.
Under this competition, the transaction volume without priority fees gradually failed to meet the attacker’s goal. As a result, there were several cases mentioned at the beginning where transactions with priority fees were still attacked.
Taking this transaction as an example, the victim paid a priority fee of 0.000075 SOL, which seemed to be immune to attacks in the past. But now the sandwich attacker paid a higher fee, which was raised to 0.0044 SOL. In this transaction, the user tried to make a transaction worth about 5 SOL, and the attacker took away 0.08 SOL.
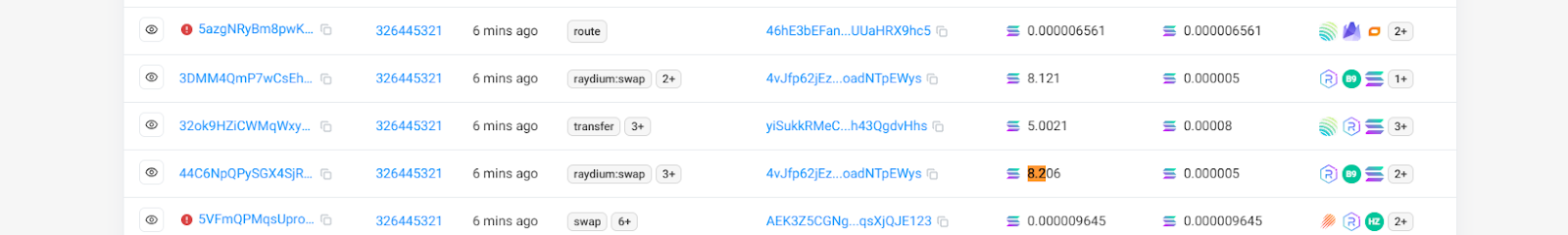
In fact, based on the investigation of multiple attack transactions, we found that the attacked users generally adopted a priority fee standard of less than 0.001SOL, and were therefore attacked.
In this process, there is another point that needs to be explained, that is, the attacker's method has also changed. In the past, sandwich attackers generally used the method of bundling transactions, that is, packaging those transactions that did not pay the priority fee into a transaction package. In this bundle, the attacker who submitted the transaction can arrange the order at will. But now, since most users will pay a certain priority fee, it will not be packaged into other transactions, so it can be found by observing the chain. Most of the current sandwich attacks use a non-bundling method, but instead initiate two transactions independently before and after this transaction. Therefore, the amount of the priority fee becomes a very critical criterion.
In summary, the evolution of sandwich attacks on the Solana chain has changed from a situation in which one could avoid being bundled by paying a priority fee to a situation in which one could be inserted into transactions before or after as long as the priority fee paid was insufficient.
For users, the next choice is no longer whether to pay the priority fee, but whether to pay enough. It seems that this has entered the cycle described above.
Only by continuously increasing the priority fee can the node maintain the original profit level when the transaction volume shrinks. On the other hand, if the user is unwilling to compromise, then he will only lose more principal.
The risk of node leakage exacerbates the ecological dilemma
However, there is also a prerequisite in this process, that is, the node leading the block must cooperate with the sandwich attacker to leak data, so that the attacker can know in advance the transactions that have paid the priority fee. Starting from February 27, the founder of Pepe boost called on Solana officials to pay attention to this matter on the X platform. In addition, GMGN co-founder and PinkPunkBot publicly raised similar questions on social media. However, as of March 13, Solana officials have not responded to this.
As of March 10, the daily priority fee on the Solana chain has dropped to around 14,000 SOL, down more than 92% from the high of 183,000 SOL in January.
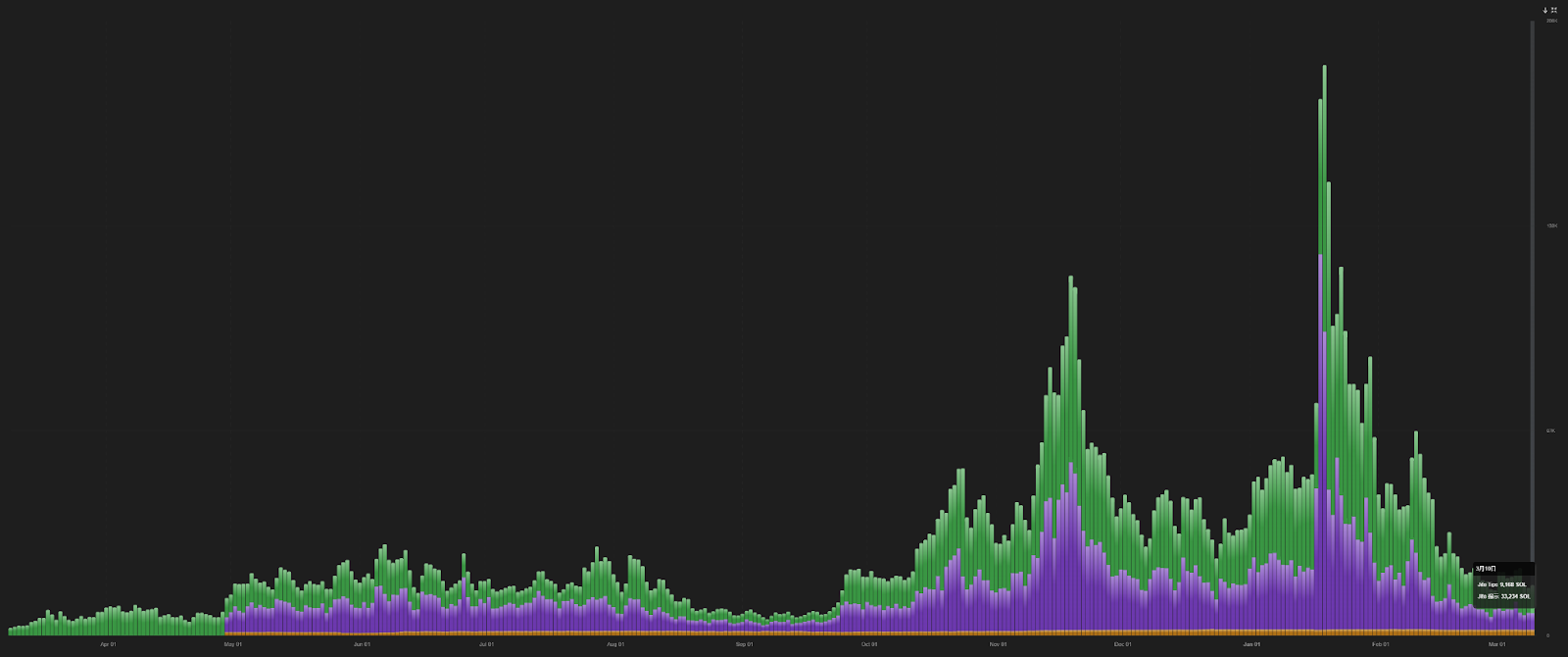
The number of active addresses on the Solana chain also dropped to 2.14 million, a 75% drop from the peak of 8.78 million. In an already extremely shrinking market environment, continuing to allow sandwich attacks is obviously tantamount to draining the pond to catch fish, further driving users away from the Solana ecosystem.
The competition among public chains has never been limited to the arms race of TPS numbers, but also depends on whether the participants in the ecosystem can establish a sustainable consensus on value. At a time when transaction volume has plummeted and priority fee income has shrunk, Solana is facing a difficult situation: if the MEV interest group is allowed to continue to devour user assets, the network activity established by MEME in the past year may be difficult to reappear. If you exhaust the pond to fish, there will be no fish in the end.
You May Also Like

Ethereum unveils roadmap focusing on scaling, interoperability, and security at Japan Dev Conference

Here’s How Consumers May Benefit From Lower Interest Rates
