Plug-and-Play LM Checkpoints with TensorFlow Model Garden
Content Overview
- Install TF Model Garden package
- Import necessary libraries
- Load BERT model pretrained checkpoints
- Select required BERT model
- Construct BERT Model Using the NEW params.yaml
- Construct BERT Model Using the old bert_config.json
- Construct a Classifier with encoder_config
- Load Pretrained Weights into the BERT Classifier
- Load ALBERT model pretrained checkpoints
- Construct ALBERT Model Using the New params.yaml
- Construct ALBERT Model Using the Old albert_config.json
- Construct a Classifier with encoder_config
- Load Pretrained Weights into the Classifier
- Load ELECTRA model pretrained checkpoints
- Construct BERT Model Using the NEW params.yaml
- Construct a Classifier with encoder_config
- Load Pretrained Weights into the Classifier
\ \ This tutorial demonstrates how to load BERT, ALBERT and ELECTRA pretrained checkpoints and use them for downstream tasks.
Model Garden contains a collection of state-of-the-art models, implemented with TensorFlow's high-level APIs. The implementations demonstrate the best practices for modeling, letting users to take full advantage of TensorFlow for their research and product development.
Install TF Model Garden package
pip install -U -q "tf-models-official" Import necessary libraries
import os import yaml import json import tensorflow as tf \
2023-10-17 12:27:09.738068: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9342] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2023-10-17 12:27:09.738115: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:609] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2023-10-17 12:27:09.738155: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1518] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered \
import tensorflow_models as tfm from official.core import exp_factory Load BERT model pretrained checkpoints
Select required BERT model
# @title Download Checkpoint of the Selected Model { display-mode: "form", run: "auto" } model_display_name = 'BERT-base cased English' # @param ['BERT-base uncased English','BERT-base cased English','BERT-large uncased English', 'BERT-large cased English', 'BERT-large, Uncased (Whole Word Masking)', 'BERT-large, Cased (Whole Word Masking)', 'BERT-base MultiLingual','BERT-base Chinese'] if model_display_name == 'BERT-base uncased English': !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == 'BERT-base cased English': !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == "BERT-large uncased English": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/uncased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "uncased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == "BERT-large cased English": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == "BERT-large, Uncased (Whole Word Masking)": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/wwm_uncased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "wwm_uncased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == "BERT-large, Cased (Whole Word Masking)": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/wwm_cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "wwm_cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == "BERT-base MultiLingual": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/multi_cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "multi_cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" elif model_display_name == "BERT-base Chinese": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz" \
--2023-10-17 12:27:14-- https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/bert/v3/cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz Resolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 172.217.219.207, 209.85.146.207, 209.85.147.207, ... Connecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|172.217.219.207|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 401886728 (383M) [application/octet-stream] Saving to: ‘cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz’ cased_L-12_H-768_A- 100%[===================>] 383.27M 79.4MB/s in 5.3s 2023-10-17 12:27:19 (72.9 MB/s) - ‘cased_L-12_H-768_A-12.tar.gz’ saved [401886728/401886728] cased_L-12_H-768_A-12/ cased_L-12_H-768_A-12/vocab.txt cased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_model.ckpt.index cased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001 cased_L-12_H-768_A-12/params.yaml cased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_config.json \
# Lookup table of the directory name corresponding to each model checkpoint folder_bert_dict = { 'BERT-base uncased English': 'uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12', 'BERT-base cased English': 'cased_L-12_H-768_A-12', 'BERT-large uncased English': 'uncased_L-24_H-1024_A-16', 'BERT-large cased English': 'cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16', 'BERT-large, Uncased (Whole Word Masking)': 'wwm_uncased_L-24_H-1024_A-16', 'BERT-large, Cased (Whole Word Masking)': 'wwm_cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16', 'BERT-base MultiLingual': 'multi_cased_L-12_H-768_A-1', 'BERT-base Chinese': 'chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12' } folder_bert = folder_bert_dict.get(model_display_name) folder_bert \
'cased_L-12_H-768_A-12' Construct BERT Model Using the New params.yaml
params.yaml can be used for training with the bundled trainer in addition to constructing the BERT encoder here.
\
config_file = os.path.join(folder_bert, "params.yaml") config_dict = yaml.safe_load(tf.io.gfile.GFile(config_file).read()) config_dict \
{'task': {'model': {'encoder': {'bert': {'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'hidden_size': 768, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'intermediate_size': 3072, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'num_attention_heads': 12, 'num_layers': 12, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'vocab_size': 28996}, 'type': 'bert'} } } } \
# Method 1: pass encoder config dict into EncoderConfig encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig(config_dict["task"]["model"]["encoder"]) encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 28996, 'hidden_size': 768, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 12, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 3072, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'embedding_size': None, 'output_range': None, 'return_all_encoder_outputs': False, 'return_attention_scores': False, 'norm_first': False} \
# Method 2: use override_params_dict function to override default Encoder params encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig() tfm.hyperparams.override_params_dict(encoder_config, config_dict["task"]["model"]["encoder"], is_strict=True) encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 28996, 'hidden_size': 768, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 12, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 3072, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'embedding_size': None, 'output_range': None, 'return_all_encoder_outputs': False, 'return_attention_scores': False, 'norm_first': False} Construct BERT Model Using the Old bert_config.json
bert_config_file = os.path.join(folder_bert, "bert_config.json") config_dict = json.loads(tf.io.gfile.GFile(bert_config_file).read()) config_dict \
{'hidden_size': 768, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'intermediate_size': 3072, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'num_attention_heads': 12, 'num_layers': 12, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'vocab_size': 28996, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1} \
encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig({ 'type':'bert', 'bert': config_dict }) encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 28996, 'hidden_size': 768, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 12, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 3072, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'embedding_size': None, 'output_range': None, 'return_all_encoder_outputs': False, 'return_attention_scores': False, 'norm_first': False} Construct a classifier with encoder_config
Here, we construct a new BERT Classifier with 2 classes and plot its model architecture. A BERT Classifier consists of a BERT encoder using the selected encoder config, a Dropout layer and a MLP classification head.
\
bert_encoder = tfm.nlp.encoders.build_encoder(encoder_config) bert_classifier = tfm.nlp.models.BertClassifier(network=bert_encoder, num_classes=2) tf.keras.utils.plot_model(bert_classifier) \
2023-10-17 12:27:24.243086: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:2211] Cannot dlopen some GPU libraries. Please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly if you would like to use GPU. Follow the guide at https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu for how to download and setup the required libraries for your platform. Skipping registering GPU devices... \ 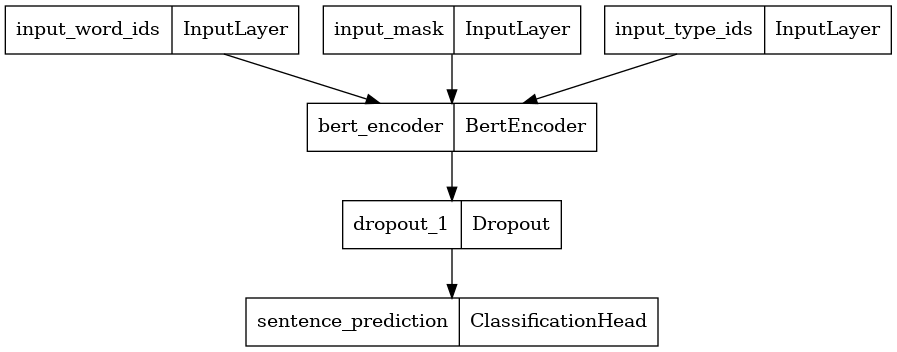
Load Pretrained Weights into the BERT Classifier
The provided pretrained checkpoint only contains weights for the BERT Encoder within the BERT Classifier. Weights for the Classification Head is still randomly initialized.
\
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(encoder=bert_encoder) checkpoint.read( os.path.join(folder_bert, 'bert_model.ckpt')).expect_partial().assert_existing_objects_matched() \
<tensorflow.python.checkpoint.checkpoint.CheckpointLoadStatus at 0x7f73f8418fd0> Load ALBERT model pretrained checkpoints
# @title Download Checkpoint of the Selected Model { display-mode: "form", run: "auto" } albert_model_display_name = 'ALBERT-xxlarge English' # @param ['ALBERT-base English', 'ALBERT-large English', 'ALBERT-xlarge English', 'ALBERT-xxlarge English'] if albert_model_display_name == 'ALBERT-base English': !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/albert/albert_base.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "albert_base.tar.gz" elif albert_model_display_name == 'ALBERT-large English': !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/albert/albert_large.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "albert_large.tar.gz" elif albert_model_display_name == "ALBERT-xlarge English": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/albert/albert_xlarge.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "albert_xlarge.tar.gz" elif albert_model_display_name == "ALBERT-xxlarge English": !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/albert/albert_xxlarge.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "albert_xxlarge.tar.gz" \
--2023-10-17 12:27:27-- https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/albert/albert_xxlarge.tar.gz Resolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 172.253.114.207, 172.217.214.207, 142.251.6.207, ... Connecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|172.253.114.207|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 826059238 (788M) [application/octet-stream] Saving to: ‘albert_xxlarge.tar.gz’ albert_xxlarge.tar. 100%[===================>] 787.79M 117MB/s in 6.5s 2023-10-17 12:27:34 (122 MB/s) - ‘albert_xxlarge.tar.gz’ saved [826059238/826059238] albert_xxlarge/ albert_xxlarge/bert_model.ckpt.index albert_xxlarge/30k-clean.model albert_xxlarge/30k-clean.vocab albert_xxlarge/bert_model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001 albert_xxlarge/params.yaml albert_xxlarge/albert_config.json \
# Lookup table of the directory name corresponding to each model checkpoint folder_albert_dict = { 'ALBERT-base English': 'albert_base', 'ALBERT-large English': 'albert_large', 'ALBERT-xlarge English': 'albert_xlarge', 'ALBERT-xxlarge English': 'albert_xxlarge' } folder_albert = folder_albert_dict.get(albert_model_display_name) folder_albert \
'albert_xxlarge' Construct ALBERT Model Using the New params.yaml
params.yaml can be used for training with the bundled trainer in addition to constructing the BERT encoder here.
\
config_file = os.path.join(folder_albert, "params.yaml") config_dict = yaml.safe_load(tf.io.gfile.GFile(config_file).read()) config_dict \
{'task': {'model': {'encoder': {'albert': {'attention_dropout_rate': 0.0, 'dropout_rate': 0.0, 'embedding_width': 128, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'hidden_size': 4096, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'intermediate_size': 16384, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'num_attention_heads': 64, 'num_layers': 12, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'vocab_size': 30000}, 'type': 'albert'} } } } \
# Method 1: pass encoder config dict into EncoderConfig encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig(config_dict["task"]["model"]["encoder"]) encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 30000, 'embedding_width': 128, 'hidden_size': 4096, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 64, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 16384, 'dropout_rate': 0.0, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.0, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02} \
# Method 2: use override_params_dict function to override default Encoder params encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig() tfm.hyperparams.override_params_dict(encoder_config, config_dict["task"]["model"]["encoder"], is_strict=True) encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 30000, 'embedding_width': 128, 'hidden_size': 4096, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 64, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 16384, 'dropout_rate': 0.0, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.0, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02} Construct ALBERT Model Using the Old albert_config.json
albert_config_file = os.path.join(folder_albert, "albert_config.json") config_dict = json.loads(tf.io.gfile.GFile(albert_config_file).read()) config_dict \
{'hidden_size': 4096, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'intermediate_size': 16384, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'num_attention_heads': 64, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'vocab_size': 30000, 'embedding_width': 128, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.0, 'dropout_rate': 0.0, 'num_layers': 12, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu'} \
encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig({ 'type':'albert', 'albert': config_dict }) encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 30000, 'embedding_width': 128, 'hidden_size': 4096, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 64, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 16384, 'dropout_rate': 0.0, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.0, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02} Construct a Classifier with encoder_config
Here, we construct a new BERT Classifier with 2 classes and plot its model architecture. A BERT Classifier consists of a BERT encoder using the selected encoder config, a Dropout layer and a MLP classification head.
\
albert_encoder = tfm.nlp.encoders.build_encoder(encoder_config) albert_classifier = tfm.nlp.models.BertClassifier(network=albert_encoder, num_classes=2) tf.keras.utils.plot_model(albert_classifier) \ 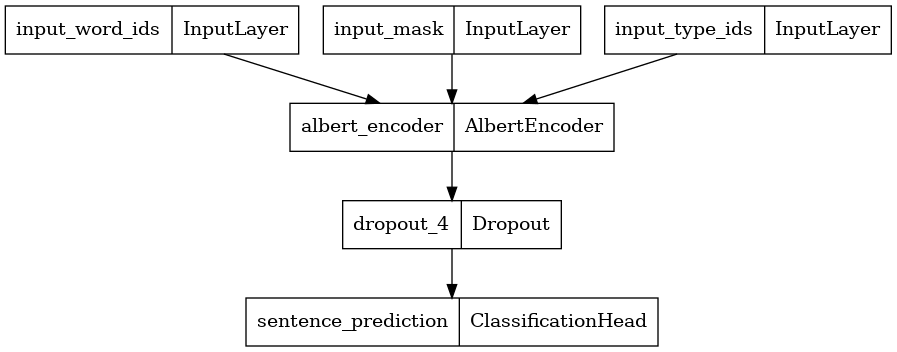
Load Pretrained Weights into the Classifier
The provided pretrained checkpoint only contains weights for the ALBERT Encoder within the ALBERT Classifier. Weights for the Classification Head is still randomly initialized.
\
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(encoder=albert_encoder) checkpoint.read( os.path.join(folder_albert, 'bert_model.ckpt')).expect_partial().assert_existing_objects_matched() \
<tensorflow.python.checkpoint.checkpoint.CheckpointLoadStatus at 0x7f73f8185fa0> Load ELECTRA model pretrained checkpoints
# @title Download Checkpoint of the Selected Model { display-mode: "form", run: "auto" } electra_model_display_name = 'ELECTRA-small English' # @param ['ELECTRA-small English', 'ELECTRA-base English'] if electra_model_display_name == 'ELECTRA-small English': !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/electra/small.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "small.tar.gz" elif electra_model_display_name == 'ELECTRA-base English': !wget "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/electra/base.tar.gz" !tar -xvf "base.tar.gz" \
--2023-10-17 12:27:45-- https://storage.googleapis.com/tf_model_garden/nlp/electra/small.tar.gz Resolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 172.253.114.207, 172.217.214.207, 142.251.6.207, ... Connecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|172.253.114.207|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 157951922 (151M) [application/octet-stream] Saving to: ‘small.tar.gz’ small.tar.gz 100%[===================>] 150.63M 173MB/s in 0.9s 2023-10-17 12:27:46 (173 MB/s) - ‘small.tar.gz’ saved [157951922/157951922] small/ small/ckpt-1000000.data-00000-of-00001 small/params.yaml small/checkpoint small/ckpt-1000000.index \
# Lookup table of the directory name corresponding to each model checkpoint folder_electra_dict = { 'ELECTRA-small English': 'small', 'ELECTRA-base English': 'base' } folder_electra = folder_electra_dict.get(electra_model_display_name) folder_electra \
'small' Construct BERT Model Using the params.yaml
params.yaml can be used for training with the bundled trainer in addition to constructing the BERT encoder here.
\
config_file = os.path.join(folder_electra, "params.yaml") config_dict = yaml.safe_load(tf.io.gfile.GFile(config_file).read()) config_dict \
{'model': {'cls_heads': [{'activation': 'tanh', 'cls_token_idx': 0, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'inner_dim': 64, 'name': 'next_sentence', 'num_classes': 2}], 'disallow_correct': False, 'discriminator_encoder': {'type': 'bert', 'bert': {'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'embedding_size': 128, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'hidden_size': 256, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'intermediate_size': 1024, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'num_attention_heads': 4, 'num_layers': 12, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'vocab_size': 30522} }, 'discriminator_loss_weight': 50.0, 'generator_encoder': {'type': 'bert', 'bert': {'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'embedding_size': 128, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'hidden_size': 64, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'intermediate_size': 256, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'num_attention_heads': 1, 'num_layers': 12, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'vocab_size': 30522} }, 'num_classes': 2, 'num_masked_tokens': 76, 'sequence_length': 512, 'tie_embeddings': True} } \
disc_encoder_config = tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig( config_dict['model']['discriminator_encoder'] ) disc_encoder_config.get().as_dict() \
{'vocab_size': 30522, 'hidden_size': 256, 'num_layers': 12, 'num_attention_heads': 4, 'hidden_activation': 'gelu', 'intermediate_size': 1024, 'dropout_rate': 0.1, 'attention_dropout_rate': 0.1, 'max_position_embeddings': 512, 'type_vocab_size': 2, 'initializer_range': 0.02, 'embedding_size': 128, 'output_range': None, 'return_all_encoder_outputs': False, 'return_attention_scores': False, 'norm_first': False} Construct a Classifier with encoder_config
Here, we construct a Classifier with 2 classes and plot its model architecture. A Classifier consists of a ELECTRA discriminator encoder using the selected encoder config, a Dropout layer and a MLP classification head.
\
:::tip Note: The generator is discarded and the discriminator is used for downstream tasks
:::
\
disc_encoder = tfm.nlp.encoders.build_encoder(disc_encoder_config) elctra_dic_classifier = tfm.nlp.models.BertClassifier(network=disc_encoder, num_classes=2) tf.keras.utils.plot_model(elctra_dic_classifier) \ 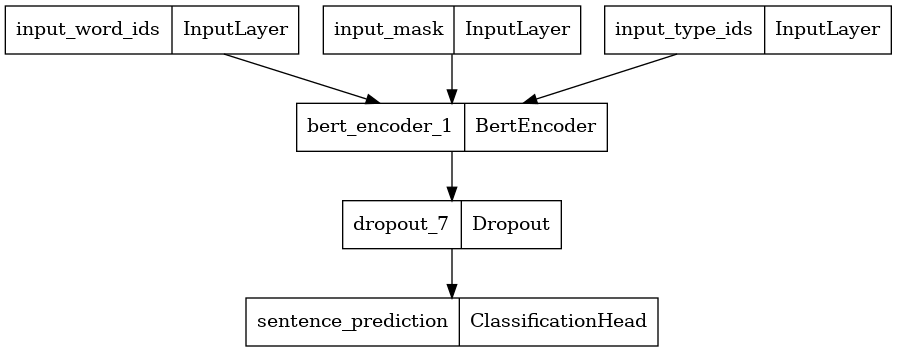
Load Pretrained Weights into the Classifier
The provided pretrained checkpoint contains weights for the entire ELECTRA model. We are only loading its discriminator (conveninently named as encoder) wights within the Classifier. Weights for the Classification Head is still randomly initialized.
\
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(encoder=disc_encoder) checkpoint.read( tf.train.latest_checkpoint(os.path.join(folder_electra)) ).expect_partial().assert_existing_objects_matched() \
<tensorflow.python.checkpoint.checkpoint.CheckpointLoadStatus at 0x7f74dbe84f40> \ \
:::info Originally published on the TensorFlow website, this article appears here under a new headline and is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Code samples shared under the Apache 2.0 License.
:::
\
You May Also Like

‘Love Island Games’ Season 2 Release Schedule—When Do New Episodes Come Out?

Trend Research has liquidated its ETH holdings and currently has only 0.165 coins remaining.
